Dust class H
What does dust class H mean?
Filters and extraction systems are both classified in dust classes. Consider the preferred degree of separation, which has to be achieved, and the type of dusts, which has to be removed. Filters of class H are particularly effective and work for very small particles like hazardous dusts. The dust classes are divided into three groups, which are L, M and H. For the filter dust classes, L defines coarse-grained, M slightly finer and H the finest dust, while the dust classes regulate the use of the systems.
Dust classes overview
|
Dust classes of filter and extraction systems |
Usable for |
Fielding |
|
L – slightly hazardous dusts |
Common house dust, sand, gypsum, lime, as well as allergenic substances such as mite and pollen |
Household |
|
M – medium hazardous dusts |
Wood dust, paint particles and various metal dusts |
Small companies, for more control and transparency |
|
H – highly hazardous dusts |
Suitable for highly dangerous and carcinogenic substances such as mold spores, lead dust, mineral fibers |
Companies with hazardous substances, extremely well filtration, highest security |
Safety vacuum cleaners that comply with dust class H can only draw in asbestos dusts. In Germany, these cleaners must additionally fulfill the requirements of TRGS 519 No. 7.2 par. 6. Special vacuum cleaners are used, which have been particularly approved for explosive and flammable dusts, in accordance with the ATEX directives. Classes L and M may be used for non-carcinogenic dusts with AGW values > 1.0 mg / m³ or flammable dusts for applications in ATEX zone 22.
Generally note:
In general, it should be noted that a large part of the risk of unrecognized particles originates at the point of origin. If only 80% are captured at the point of origin, the regulation of the degree of separation is not expedient. It is important to ensure the correct lead of supply air and exhaust air with the aid of indoor air measures in order to ensure a sufficient supply of fresh air. Turbulences may occur.Since 1998, the international standard DIN EN 60335-2-69 has been used as the base of evaluation for dust-removing machines (SBM) in industrial uses. It defines the intended suitability of the devices and classifies them according to the different testing basics. With the new Hazardous Substances Ordinance, the values of the “Maximum Workplace Concentration” (MAK) were replaced by the AGW limits. DIN EN 60335-2-69 differentiates between dry, unhealthy and flammable dusts and assesses their classifications. The guidelines for ventilation and air conditioning systems (RLT) of July 2011 apply to a system certification.
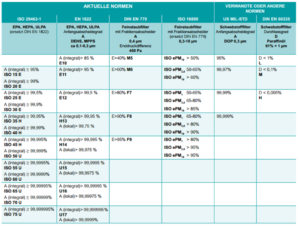
The dust class H according to DIN EN 60335-2-69 as a filter class is not comparable with the generally known filter classes according to DIN EN1822. The guidelines mentioned are based on various measurement and test regulations that work with different test aerosols, measuring methods and particle sizes. It is thus possible for a filter according to DIN EN1822-E10 to meet the requirements of a dust class H deposition in measurements. This is due to the fact that the specified permeability of 0.005% has nothing to do with the filtration efficiency of 99.995% of the filter class H14 (according to EN1822).
Test aerosols with particle distributions of 0.1-0.3μm are used in EN1822, 99.95% for filter class H13 and 99.995% for H14. Filters are 100% tested. Currently, no test standard with particle measurements smaller than 0.1μm is available. It is to assume that smaller particles do not simply migrate through the filter material, but are attracted to the mass attraction of the filter grid. The particle filters used by TBH according to EN1822 with a separation efficiency of H13 are the best protection against particles of any kind and even exceed the requirements of DIN EN ISO 15012-1.
Dust concentration
| Dust concentration |
EN 60335-2-69, IEC 335-2-69 |
||
|
AGW limit from 2005 |
MAK limit until 2005 |
Dust class |
max. transmittance |
|
Dusts AGW > 1mg/m³ |
Dusts MAK > 1mg/m³ |
L |
1% |
|
Dusts and wood dust AGW > 0,1 mg/m³ |
Dusts and wood dust MAK > 0,1 mg/m³ |
M |
0,1% |
|
Carcinogenic dusts AGW < 0,1 mg/m³ |
Carcinogenic dusts MAK < 0,1 mg/m³ |
H |
0,005% |
|
Highly carcinogenic dusts AGW < 0,1 mg/m³ |
Highly carcinogenic dusts MAK < 0,1 mg/m³ |
H + suitability |
0,005% |
Table of valid norms
Comparison of the filter separation classes according to different valid standards. (Click on image to enlarge it)
Do you have any further questions?Please call us at +49 (0) 7082/9473-0 or send us an e-mail to info@tbh.eu.